What Is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process where computers solve difficult mathematical puzzles to verify and record Bitcoin transactions on the public ledger (blockchain), and in return they’re rewarded with newly created bitcoins.
Bitcoin mining is like a digital treasure hunt where powerful computers race to solve tricky math puzzles. When a computer successfully solves one, it gets two jobs done at once:
- Checks and records who sent the Bitcoin and to whom it was sent to.
- Earns new Bitcoin as a reward for doing the work.
This is a fundamental part of the Bitcoin network as it ensures security, transparency and give the control to use single person using the network instead of one person or an organization.
How Does It Work?
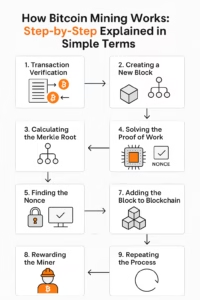
Bitcoin mining involves several key steps that ensure transactions are securely added to the blockchain and new bitcoins are generated as a reward for miners. Here’s an overview of the entire process
1. Transaction Verification: People around the world send Bitcoin to each other. These transactions are sent to the network, and these computers (miners) check to make sure they’re real. this is to confirm is someone has enough money before they spend it.
2. Creating a New Block: Verified transactions are grouped together into a “block”—like a page in a digital notebook that records several transactions.
3. Calculating the Merkle Root: All the transactions in the block are turned into short codes and then combined together into one single code called the Merkle Root. This root summarizes all the transactions in that block with one fingerprint.
4. Solving the Proof of Work: Now miners start a race to solve a difficult puzzle (this is the “proof of work”). It’s like guessing a really long combination lock. It takes a lot of computing power and energy.
5. Finding the Nonce: To solve the puzzle, miners try different numbers called nonces (like keys) until they find one that makes the block’s code (called a hash) start with a certain number of zeroes. The right nonce is the winning combination.
6. Validation by the Network: Once a miner finds the correct nonce, they shout it to the whole network. Other computers double-check the answer to make sure it’s correct.
7. Adding the Block to the Blockchain: If the answer is right, the new block is added to the end of the blockchain—a chain of blocks that records every Bitcoin transaction ever made.
8. Rewarding the Miner: The winning miner gets rewarded with newly created Bitcoin and transaction fees from the block. It’s like a thank-you for doing the hard work.
9. Repeating the Process: After that, the whole process starts again with new transactions waiting to be verified and recorded.
Start Mining Bitcoin Today
Why is Mining Important?
1. Securing the Network
Mining helps keep Bitcoin safe from hackers and fraud. The Bitcoin network is decentralized—meaning no single person or company controls it. Because anyone can join, this makes it almost impossible for dishonest users to cheat the system. Mining uses computing power and energy to make it extremely hard to change any part of the blockchain (Bitcoin’s record book). To hack it, someone would need to control more than 50% of all the mining power worldwide—which is nearly impossible and very expensive.
In short: Mining makes Bitcoin very secure by making cheating too difficult and costly.
2. Confirming and Recording Transactions
Every time you send or receive Bitcoin, the transaction needs to be verified. Miners collect these transactions, check if they’re valid (like if the sender actually has the Bitcoin), and group them into a block. Once a block is confirmed (mined), it gets permanently added to the blockchain, and the transactions can’t be changed. Why it matters: Without miners, transactions would not be processed or confirmed—and Bitcoin would stop working. This is an integral part of the blockchain system.
3. Creating New Bitcoins
Mining is the only way that new bitcoins are created. Just like gold is mined from the earth, new bitcoins are “mined” by solving complex math puzzles. When a miner successfully adds a block, they get rewarded with newly created bitcoins (plus some transaction fees).
This process continues until the total supply of 21 million bitcoins is reached. This matters because: It controls how new bitcoins enter the system and keeps inflation under control—like a predictable money supply.
In summary:Validating transaction information, maintaining the integrity of the blockchain and opening new blocks are the main purpose for mining, while the Bitcoin reward is the incentive to mine.
The History and Future of Bitcoin Mining
Who Created Bitcoin?
The invention of bitcoin is famously attributed to “Satoshi Nakamoto,” a nickname used by the author of the bitcoin white paper published in 2008.
When Did Bitcoin Mining Begin?
The very first Bitcoin block called the Genesis Block was mined by Satoshi Nakamoto on January 3, 2009.
The reward was 50 bitcoins per block. At the time, mining could be done with a regular computer (CPU mining). This is because as of then, not many people where mining bitcoin thus the competition was low.
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin has a rule where the mining reward cuts in half every 210,000 blocks (roughly every 4 years).
This is called Bitcoin Halving, and it helps control inflation by slowly reducing how many new bitcoins are created. Halving has a great influence on the price of bitcoin as reducing the supply periodically gives it more value.
Bitcoin Halving history:
2009: 50 BTC per block
2012: 25 BTC
2016: 12.5 BTC
2020: 6.25 BTC
2024: 3.125 BTC (current reward in 2025)
How Many Bitcoins Will Ever Exist?
Only 21 million bitcoins will ever be mined no more, ever.
This fixed limit is built into the code, making Bitcoin scarce like gold.
As of 2025, over 19.7 million BTC have already been mined.
When Will Bitcoin Mining End?
Mining will continue until the last bitcoin is mined estimated around the year 2140.
After that, no new bitcoins will be created.
How Will the Network Survive After Mining Ends?
When new bitcoins stop being issued, miners will start to earn transaction fees from users. These fees will the incentive to keep miners running and the network secure. Miners will still verify transactions and secure the network. They’ll just get paid with fees only, not new bitcoins.
Is Bitcoin Mining Still Profitable?
Mining profitability depends on several factors:
- Electricity costs
- Hardware efficiency
- Bitcoin’s current price
- Network difficulty
Final Thoughts
Bitcoin mining is the backbone of the Bitcoin network. While it requires technical know-how and investment, it plays a crucial role in keeping the network secure and operational. As Bitcoin continues to grow, so does the importance of miners in shaping its future.